Loading component...
The seventh wave of the Michigan State University Food Literacy and Engagement Poll sampled 2,001 Americans on their attitudes and knowledge of food, agriculture and climate change. Notably, 41% say they never or rarely seek information about where their food was grown or how it was produced.
“As a nation, we celebrate our long history of farming and food production, yet so many of us have not been paying attention to how agricultural practices and emerging technologies sustain us,” said Sheril Kirshenbaum, co-director of the biannual survey. “The global food system also plays a very significant role in addressing climate challenges, but our results indicate that most Americans are not aware of the relationships between our diets and the planet.”
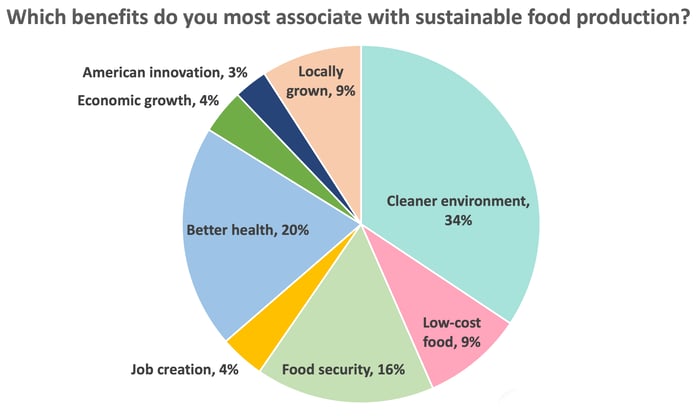
The March 2021 poll results reveal that 23% of Americans mistakenly believe that transportation produces the most greenhouse gas emissions in food production, even though it only accounts for 6%. Meanwhile 61% thought reducing pesticide use would limit the food system’s impact on climate change. While the use of pesticides has posed environmental problems, Kirshenbaum said it is not a big contributor to greenhouse gas emissions compared to other factors.
Read more about the results of the poll on the AgBioResearch website.